close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-22 Origin: Site

Chromium zirconium copper is special for tough jobs. It has high electrical conductivity, strong strength, and good wear resistance. It keeps these features even after heat treatment. This makes it a good choice for hard industrial work. The table below shows that copper chrome zirconium is better than other copper alloys in wear resistance and strength.
Property/Parameter | Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy | Cu-Cd Alloy | Cu-Be Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|
Wear Resistance | Highest among tested alloys | Lower than Cu-Cr-Zr | Lower than Cu-Cr-Zr |
Ultimate Tensile Strength | Up to 554 MPa | Lower | Lower |
Electrical Conductivity | 84% IACS | Lower | Lower |
Health/Safety | Safe | Cd hazard | Be hazard |
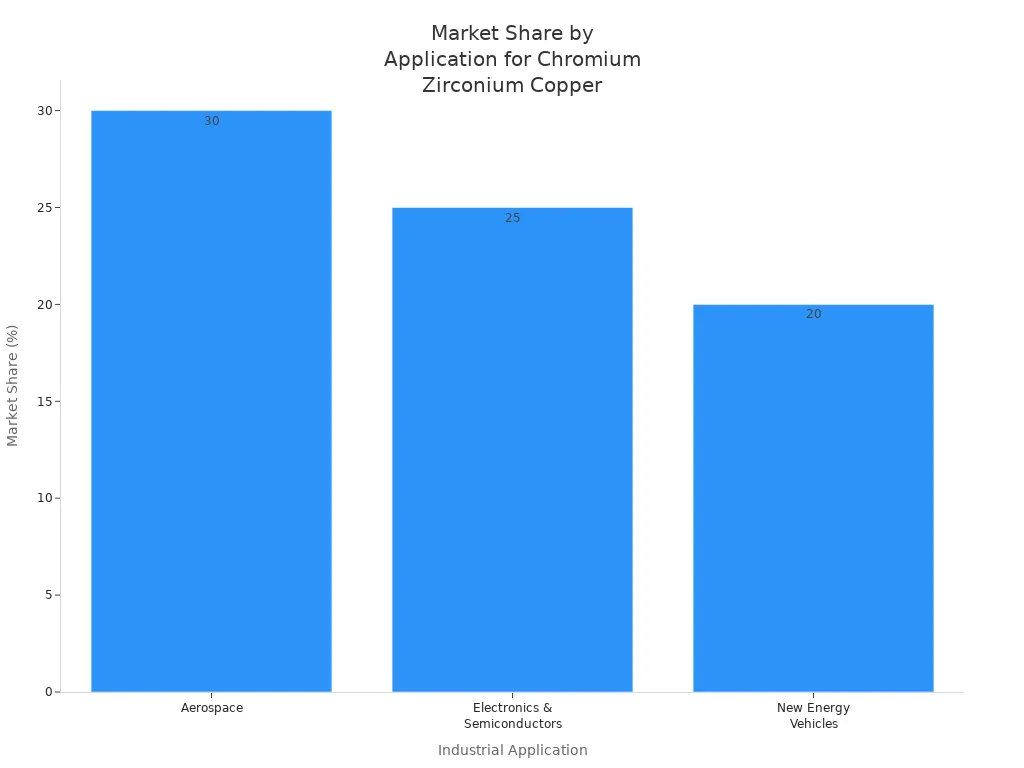
Copper chrome zirconium is used in aerospace, electronics, and new energy vehicles. The chart below shows how much it is used in these areas.
Chromium zirconium copper is very strong and conducts electricity well. It does not wear out easily, so it is good for hard jobs in factories. This alloy stays strong and keeps working after being heated. That helps it work well in welding, electronics, and hot places. It does not rust or wear down fast because chromium and zirconium protect it. This makes it last longer in tough places. Chromium zirconium copper is used a lot in cars, planes, welding, and electrical parts. It is chosen because it is tough and works well with electricity. Careful checks and rules make sure this alloy is always good quality. This makes it a good and safe choice for hard jobs.
Copper chrome zirconium is special because of its exact mix. The c18150 copper alloy is mostly copper. It also has a little chromium and zirconium. This mix helps it work well in tough places. The usual chemical makeup follows rules like ASTM B C18150 and RWMA Class II. The table below shows what is in it:
Element | Typical Range (%) | Nominal (%) |
|---|---|---|
Chromium | 0.5 - 1.5 | 1.0 |
Zirconium | 0.05 - 0.25 | 0.1 |
Copper | Balance (~98.85-98.9) | 98.9 |
This mix gives copper chrome zirconium its strength. It also stops it from sticking during welding. It helps the alloy stay strong when used for hard jobs.
The c18150 copper alloy is strong and tough. It has high tensile strength and good hardness. It can stretch a bit before breaking. These things help it keep its shape under pressure. The table below shows its main mechanical properties:
Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
Ultimate Tensile Strength | 510 | MPa |
Yield Tensile Strength | 460 | MPa |
Rockwell B Hardness | 80 | HRB |
Elongation at Break | 8.3 | % |
Elastic Modulus | 120 | GPa |
Shear Strength | 300 | MPa |
Shear Modulus | 47 | GPa |
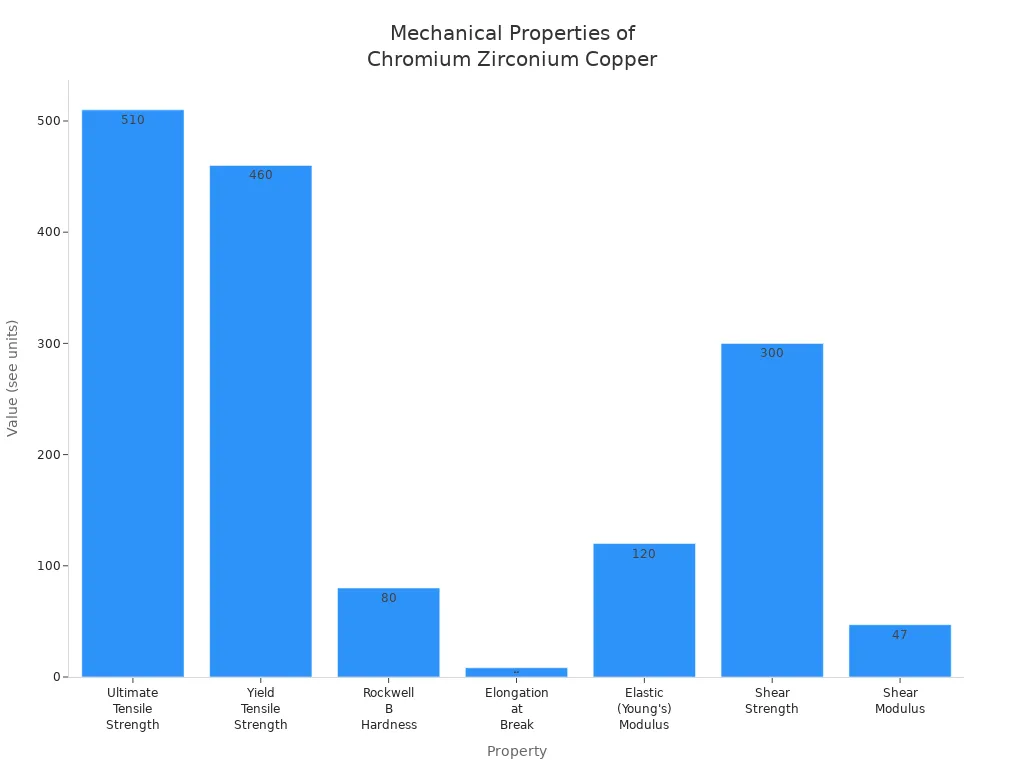
Copper chrome zirconium keeps these properties after heat treatment. This makes it great for welding and other hard jobs.
C18150 copper alloy has great physical properties. It moves electricity and heat very well. It does not get soft at high temperatures. The table below shows its main physical properties:
Property | Value (Metric) |
|---|---|
Melting Point (Liquidus) | 1080 °C |
Density | 8.89 g/cm³ |
Electrical Conductivity | 80% IACS @ 20°C |
Thermal Conductivity | 323.6 W/m·K @ 20°C |
Coefficient of Expansion | 16.45×10⁻⁶ /°C |
Modulus of Elasticity | 117,200 MPa |
Copper chrome zirconium does not corrode easily. It stays strong even in harsh places. These features help it work well in connectors, plugs, and motor commutators. It stays reliable, even with heat and stress.
The c18150 copper alloy is known for high conductivity. It keeps this even after being heated. Scientists use special microscopes to see tiny chromium particles inside the copper. These small pieces help the alloy move electricity well. When tested from 300 K to 873 K, the alloy's thermal conductivity went up by 20%. This happens because of aging and how the elements settle during heating.
If you age the c18150 copper alloy at 450 °C after pressing it hard, it gets even better at carrying electricity. Alloys like Cu-0.3%Cr-0.5%Zr and Cu-0.5%Cr-0.08%Zr get their best mix of hardness and conductivity this way. The structure becomes very fine-grained, which helps keep the alloy stable and its conductivity high.
Note: The c18150 copper alloy keeps over 80% IACS electrical conductivity after the right heat treatment. This is much higher than most other strong copper alloys.
The table below shows how electrical conductivity and strength compare in different copper materials:
Material Type | Electrical Conductivity (% IACS) | Mechanical Strength (MPa) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Pure Copper | 100 | N/A | Highest electrical conductivity among commercial metals |
Cu-Cr-Zr Alloys (e.g., C14500) | >80 | >600 | Lower conductivity than pure copper but much higher strength and softening temperature |
Other High Copper Alloys | 20% to >90% | Varies | Conductivity depends on alloying elements and processing |
The c18150 copper alloy gives a good balance of high conductivity and strength. It works well where pure copper would be too soft.
The c18150 copper alloy is very strong, especially after heat treatment. Heating it at 500 °C for one hour makes it much stronger. The ultimate tensile strength goes up to about 566 MPa. During this process, chromium and zirconium make tiny particles. These block movement inside the metal, making it harder to break.
The chart below shows how strength, stretch, hardness, and conductivity change with different treatments:
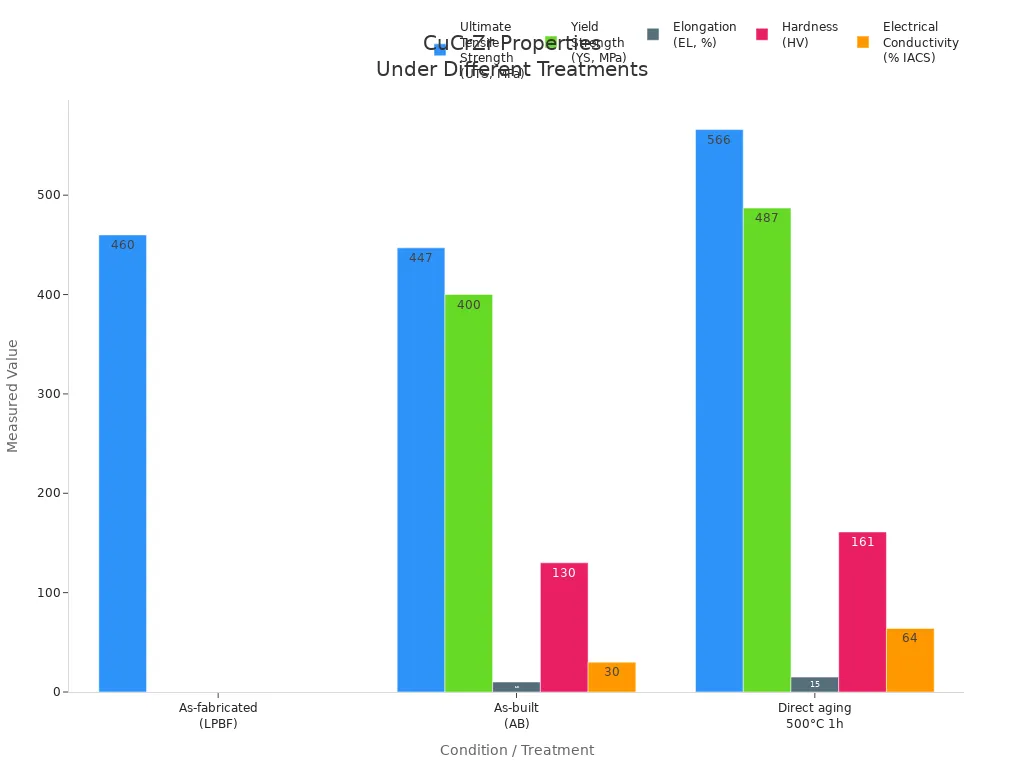
Tests on c18150 copper alloy made by laser powder bed fusion show it can reach up to 585 MPa in the transverse direction. The alloy still keeps good thermal conductivity at the same time. This makes it a strong alloy for tough jobs.
Build Orientation | Yield Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Transverse direction | 505 | 585 | 14.4 | 307 |
Build direction | 472 | 495 | 17.8 | 255 |
The c18150 copper alloy keeps its strength even after being used many times. It is good for places where both strength and conductivity are needed.
The c18150 copper alloy is great at resisting wear and corrosion. Chromium and zirconium help make a protective layer on the surface. This layer keeps the alloy safe from damage and slows down rust. Tests show that adding chromium makes the alloy resist rust better.
Chromium makes a protective layer that stops corrosion.
Zirconium makes the grains smaller, so the surface gets harder and resists wear.
The alloy's hardness goes up by about 40% when ZrC particles are there.
Corrosion current density drops by 81% in saltwater, showing strong chemical resistance.
The c18150 copper alloy keeps its wear and chemical resistance in tough places. It works well in connectors, welding electrodes, and other parts that face friction and chemicals every day.
The c18150 copper alloy is very good at handling heat. It keeps its strength and does not get soft at high temperatures. The alloy has about 0.7-0.8% chromium and 0.08-0.11% zirconium. These elements help make small, stable particles during aging. These particles stop the alloy from losing strength when it gets hot.
Aspect | Evidence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Alloy Composition | Cu-Cr-Zr alloy with ~0.7-0.8 wt.% Cr and 0.08-0.11 wt.% Zr | Helps the alloy stay strong and stable when heated |
Ageing Treatment | Peak ageing at 723 K for 3 hours | Keeps the most strength after heating |
Precipitates Identified | Fine, stable Cu5CrZr and Cu4Zr phases | These particles stop the alloy from getting weak at high temperatures |
Microhardness Evolution | Two ageing peaks at 673 K and 723 K; over-ageing at 773 K | The alloy stays hard up to a point, then gets softer if heated too much |
Microstructural Stability | Electron microscopy confirms stable precipitate morphology at elevated temperatures | Shows the alloy's heat resistance |
Application Relevance | Used as heat sink material for ITER fusion reactor | Proves it works well in real high-heat situations |
The c18150 copper alloy keeps its strength and conductivity after being hot for a long time. It does not get soft or lose shape, even above 300–400 °C. This makes it a great choice for jobs that need heat resistance and stability.
Tip: The c18150 copper alloy's mix of high conductivity, strength, wear resistance, and chemical resistance makes it perfect for tough, hot jobs.
Chromium zirconium copper is used in many fields. It is important in cars, planes, electronics, and ships. This alloy works well in wet and harsh places. Companies use it for welding electrodes and electrical contacts. It is also used in engine parts and chemical machines. The alloy is strong and does not rust easily. It stays stable after aging treatment. This helps machines last longer. Studies show it is used in trains, 5G, new energy cars, and medical tools. Because it can do so much, it is chosen for many jobs.
Industry | Application Areas | Performance Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Automotive | Electrical components | High conductivity, durability |
Aerospace | Engine parts, turbine blades | High strength, temperature resistance |
Welding Industry | Electrodes | Wear resistance, conductivity |
Many electrical parts are made with chromium zirconium copper. These include connectors and terminals. It is also used in switchgear and circuit breakers. High-tech chips use this alloy too. It handles heat well and lets electricity flow easily. The alloy does not wear out or break quickly. Connectors made from it last a long time. They work well even when used a lot. The alloy's mix of strength and conductivity helps power systems and heat exchangers.
Note: C18150 keeps its good features at high heat. This makes it great for machines that need both strength and conductivity.
Chromium zirconium copper is common in resistance welding. It stands up to heat and stays hard. It does not rust easily. Its structure stops electrodes from sticking during welding. The alloy keeps its shape and lets electricity flow well. This means electrodes last longer and welds are better. Spot welding and seam welding use this alloy. Electrode holders also use it because it is tough.
It spreads heat evenly during welding.
It does not wear out fast.
It can be shaped easily for special jobs.
This alloy is also used for plastic molds and tools. Mold cores and inserts made from it help make more parts faster. They cool down up to 40% quicker. The alloy's strength stops molds from bending or cracking. It does not wear out or rust fast. This means less fixing and longer use. Mold makers use it for injection molding and die-casting. It is also used for forging dies. The alloy works well in hot and rough places.
Property | Benefit in Molding Operations |
|---|---|
Thermal Conductivity | Fast heat dissipation, shorter cycle times |
Mechanical Strength | Resists deformation under pressure |
Wear Resistance | Prolongs mold life |
Corrosion Resistance | Reduces maintenance needs |
Chromium zirconium copper must follow strict rules in the industry. These rules make sure every batch is high quality. Companies check the chemical mix and how strong the metal is. The table below lists what is needed:
Property/Element | Specification/Range |
|---|---|
Copper (Cu) | 98.5 – 99.5% |
Chromium (Cr) | 0.5 – 1.2% |
Zirconium (Zr) | 0.03 – 0.25% |
Other Elements | < 0.2% |
Tensile Strength | 400 – 500 MPa |
Yield Strength | 350 – 450 MPa |
Hardness | 120 – 150 HV |
Electrical Conductivity | 75 – 85% IACS |
Thermal Conductivity | 320 – 340 W/m·K |
Heat Resistance | Up to 500°C |
Elongation | 10 – 15% |
These rules help the alloy stay strong and last long. They also make sure it carries electricity well. Factories use new machines to mix the metals just right. They use special steps to keep the quality high. Every piece must meet these numbers before it can be used.
Note: If the alloy meets these rules, it can be used in many jobs like welding and electronics.
Factories use many ways to check the quality of chromium zirconium copper. They test each batch to make sure it follows all the rules. Some common checks are:
Checking the factory often while making the alloy.
Testing how the metal looks and how strong it is.
Using tests like ultrasonic, eddy current, liquid dye, and X-ray.
Testing in rooms where the temperature is controlled.
Getting better machines and teaching workers new skills.
Having a Metallurgical Engineer at the factory for help.
Following ISO 9001:2015 for good quality.
Special papers and outside tests also show the alloy is good. These include Mill Test Reports and tests like Ammonia Vapor Test (ASTM B858), Mercurous Nitrate Test (ASTM B154), and Eddy-Current Test (Practice E243). Pressure tests with water or air check if it is safe. Products usually follow ASTM and ASME rules. Each batch gets its own number so it can be tracked.
These steps help make sure chromium zirconium copper always works well for hard jobs.
Chromium zirconium copper is known for being strong and lasting a long time. It also lets electricity move through it easily. This alloy follows strict rules to make sure it is good. It works well even when jobs are hard. The table below lists its main features:
Property | Value |
|---|---|
Tensile Strength | Up to 490 MPa |
Yield Strength | Up to 390 MPa |
Hardness | 75 HRB |
Electrical Conductivity | Above 75% IACS |
Thermal Conductivity | >0.77 cal/cm·cm²/s°C |
Softening Temperature | 500°C |
These things help it do well in tough places. Many companies use it because it is dependable. You can pick this alloy if you need something strong and powerful for your work.
Chromium zirconium copper is stronger than regular copper. It does not wear out as fast. It keeps its shape at high heat. This alloy does not rust or get soft easily. That is why it is good for hard jobs.
Yes, it is great for electrical contacts. It lets electricity flow well and lasts a long time. Many companies use it in connectors and switches. It works in circuit breakers too. It can handle heat and stress without problems.
Chromium zirconium copper does not have harmful metals like cadmium or beryllium. People can touch it safely with normal safety gear. It follows safety rules for most jobs.
It works very well for welding. The alloy does not stick or bend during welding. Electrodes made from it last longer. They help make strong welds. Many factories use it for spot and seam welding.
Keep it in a dry and clean place. Do not put it near strong acids or bases. Check it often to stop rust. Most companies think it is easy to store and take care of.