close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-25 Origin: Site

Aluminium bronze is a copper alloy. It uses aluminum as the main added element. The amount of aluminum is usually between 6% and 14%. It can also have iron, silicon, or manganese. This makes it different from other bronze types. Other bronzes use tin or lead instead. Aluminium bronze is strong and tough. It does not rust easily, even in the ocean. Many industries pick aluminium bronze for its special features. It does not make sparks. It also does not react much to magnets.
The aluminium bronze market is growing fast worldwide. By 2033, it may reach about 800 million units. This is a bigger share than tin or silicon bronze.
Aluminium bronze is a strong copper alloy. It has 5% to 14% aluminum. It does not rust or wear easily. This makes it good for hard places like the ocean and factories.
It makes a layer that protects it from damage. This layer stops corrosion, especially in seawater. This helps parts like ship propellers and pumps last longer. They also need less fixing.
Aluminium bronze does not make sparks. It also does not attract magnets much. This makes it safe in places with explosions. It is also good for electrical and defense uses.
It is very strong and hard. It is better than other bronzes. Engineers use it for tough parts like gears, bearings, and landing gear bushings.
Aluminium bronze costs more money. But it lasts longer and needs fewer repairs. This saves money over time in tough places.
Aluminium bronze is part of the copper alloy group. It has aluminum as its main added element. Most types have between 5% and 14% aluminum. This amount gives aluminium bronze special features. It is strong and does not wear out fast. It also does not rust easily. These things make it good for hard jobs, like in factories or near the sea.
Experts call aluminium bronze a copper-aluminum alloy. It can also have iron, nickel, manganese, or silicon. These extra elements make it stronger and last longer. The way aluminium bronze is built changes with more aluminum. If it has less than 8% aluminum, it forms one main structure called alpha. If it has more than 8%, it forms two structures called alpha and beta. This makes it even harder and stronger.
Aluminium bronze does not just stop rust. It also stays strong in tough places, like the ocean or chemical plants.
What is inside aluminium bronze decides how it works. Copper is the main part, and aluminum comes next. Most types have 5% to 11% aluminum. Some special ones can go up to 14%. Small amounts of iron and nickel are also important.
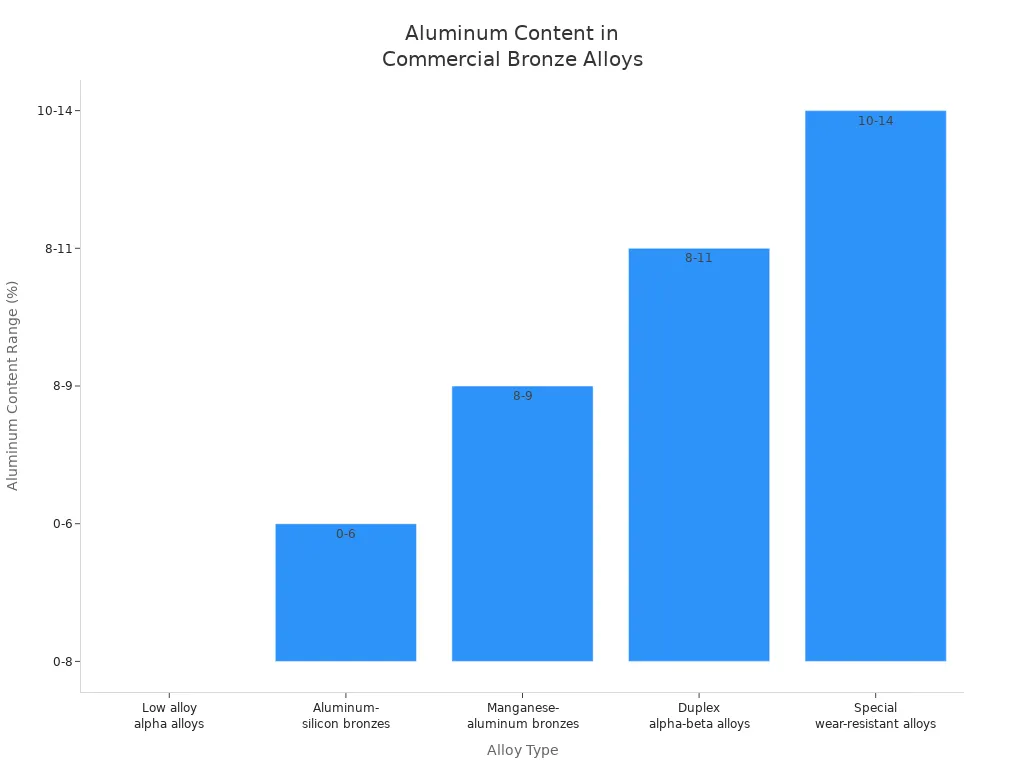
Here is a table that shows the main types of aluminium bronze and how much aluminum they have:
Alloy Type | Aluminum Content Range | Key Characteristics and Additional Elements |
|---|---|---|
Low alloy alpha alloys | < 8% | One main structure; bends without breaking |
Duplex alpha-beta alloys | 8% to 11% | Two structures; stronger; often has iron and nickel |
Special wear-resistant alloys | > 10% up to 14% | Even stronger and harder; does not wear out easily |
Aluminum-silicon bronzes | Up to ~6% | Mostly alpha structure; silicon makes it stronger and easier to shape |
Manganese-aluminum bronzes | 8% to 9% | Easy to cast; has about 13% manganese; stands up to water damage |
Small amounts of iron and nickel change how aluminium bronze is built. Iron makes hard parts that help it get stronger. Nickel helps make it even tougher and helps form a layer that protects it. These changes make it better at fighting rust and staying strong. Nickel aluminum bronze is a popular type. It uses both nickel and iron to be strong, bend without breaking, and not rust.
Nickel aluminum bronze alloys are great at fighting rust and wear. They also stay strong for a long time, even in the ocean.
Most aluminium bronze alloys have these parts:
Copper (Cu): Main metal
Aluminum (Al): 5% to 14%
Iron (Fe): Up to 5%
Nickel (Ni): Up to 5%
Manganese (Mn), Silicon (Si), Tin (Sn): Small amounts for special uses
People can change what is inside aluminium bronze to fit different jobs. For example, nickel aluminum bronze is used for ship propellers and pumps. It does not rust and stays strong. The mix of main and small parts decides how it works. This lets engineers pick the best type for each job.
Aluminum bronze is known for being very strong and hard. It is stronger than most other copper-based metals. The table below shows how strong some common types are:
Alloy Type | Common Grades | Typical Tensile Strength (MPa) | Typical Tensile Strength (psi) |
|---|---|---|---|
Aluminum Bronze | C95400, C95500, C63000 | 520 – 800 | 75,000 – 116,000 |
Nickel Aluminum Bronze | C95510, C95800, C63020 | 650 – 900+ | 94,000 – 130,000+ |
These numbers help explain why engineers use aluminum bronze for tough jobs. They need metals that can hold up under heavy weight and pressure. Aluminum bronze is stronger and harder than phosphor bronze and silicon bronze. The chart below shows how these metals compare:
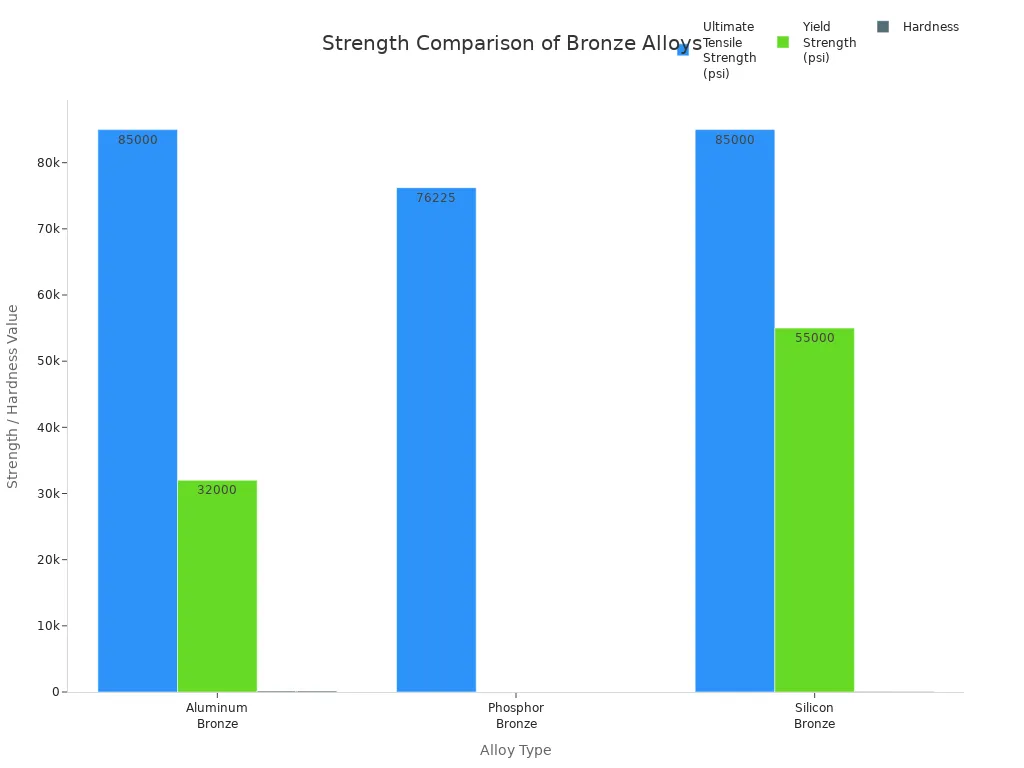
Aluminum bronze can handle a lot of pulling force before breaking. Its strength and hardness make it great for parts that must last a long time.
Aluminum bronze does not rust easily in many places. It forms a thin, strong layer on its surface. This layer protects it from rust and chemicals. Because of this, it works well in seawater and chemical plants.
Environment Condition | Flow Velocity (m/s) | Corrosion Rate (mm/year) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Seawater (low flow) | < 4.3 | 0.015 – 0.05 | Long-term steady-state corrosion rate under quiet, tidal, or flowing seawater |
Seawater (moderate flow) | 7.6 | 0.5 – 2 | Corrosion rate can rise locally up to 2 mm/year due to damage to protective oxide film |
Seawater (high flow/turbulence) | 7.6 – 30.5 | 0.5 – 0.76 (up to 2) | Corrosion rate increases logarithmically with velocity; protective film damage occurs |
Acidic environments | N/A | Not specified | Advantages noted but no quantitative corrosion rate data provided |
Aluminum bronze is better than most copper alloys in the ocean. Its special layer stops small holes and keeps it from breaking down, even in salty water. It is also better than high tensile brasses, stainless steels, and manganese bronze at fighting rust and wear from water. This makes it a top pick for ship propellers, underwater bolts, and pump parts.
Aluminum bronze is better than tin bronze and manganese bronze in tough sea water. It stays strong and keeps looking good when other metals might fail.
Aluminum bronze does not wear out or crack easily. It keeps its shape and smooth surface even after being used for a long time. The table below shows some important facts about popular types:
Alloy | Density (kg/dm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness (HBW) | Coefficient of Friction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
AMPCO® M4 | 7.45 | 1000 | 793 | 8 | 286 | 0.23 |
AMPCO® 45 | 7.53 | 814 | 517 | 15 | 228 | 0.25 |
AMPCO® 18 | 7.45 | 724 | 365 | 14 | 192 | 0.18 |
AMPCO® 8 | 7.95 | 565 | 358 | 35 | 152 | N/A |
Aluminum bronze can take a lot of repeated stress without breaking. It resists wearing down because it has hard spots inside, like Al2O3. In tests, aluminum bronze coatings almost stopped sliding wear, just like special oils do. It even did better than manganese bronze, even though it is not as hard.
Aluminum bronze is good for parts that rub together, like gears, bushings, and bearings.
Aluminum bronze has more good points besides strength and rust resistance. Here are some special features:
Non-sparking: It does not make sparks when hit, so it is safe in places where things might explode.
Low magnetic permeability: It does not get magnetized easily, so it is good for electrical and sensitive tools.
Good machinability: Aluminum bronze types like C95400 are easy to shape with sharp tools. They can be cut and finished smoothly if handled with care.
Oxidation resistance: It does not change much at high heat, so it keeps its good qualities even when hot.
These features make aluminum bronze useful in many fields. It is strong, does not wear out fast, and does not rust easily. It also does not spark or get magnetized.
Aluminum bronze is a great choice for many jobs. It works well in the ocean, factories, and electrical work where strength and lasting power are needed.
Aluminum bronze is often used on ships and in the ocean. Shipbuilders pick it because it lasts a long time. It makes a thin layer that protects it from seawater. This layer helps stop rust and keeps sea life from sticking to it. Nickel aluminum bronze is a special kind. It is good for propellers, valves, and pumps. It does not crack or stick when stressed. It is strong and does not wear out fast. That is why it is used for bushings and bearings in seawater.
Main reasons to use aluminum bronze in marine parts:
It does not rust in seawater.
It stops sea life from growing on it.
It is strong and does not wear down.
It needs little care and saves money over time.
Nickel aluminum bronze propellers are lighter than brass ones. This helps ships use less energy.
Many factories use aluminum bronze for tough machines. It works well when things get hot or heavy. Steel mills use it for bushings, gears, and pump parts. Its hardness helps it last longer in rough places. C95400 aluminum bronze is used for bushings, valves, and bearings. It means less fixing and longer use.
Common uses are:
Connecting rod bushings
Worm gears
Pump and valve parts
Bearings for big machines
Aluminum bronze is tough and easy to shape. That is why it is picked for important machine parts.
Aerospace engineers use aluminum bronze for safe parts. It is found in landing gear bushings and engine bearings. It is also used in flight control actuators. It is strong and does not break from repeated use. It can hold heavy loads and meets strict rules for planes.
Aerospace Component | Reason for Use |
|---|---|
Landing gear bushings | Strong and does not break easily |
Engine spacer bearings | Does not wear out or rust |
Flight control actuators | Handles hits and rubbing |
Brake and wheel parts | Lasts under stress |
Defense workers use aluminum bronze for tools and armor. It does not make sparks, so it is safe in risky places. It is not magnetic and does not wear out or rust. This makes it good for tough defense jobs.
Aluminum bronze tools help keep people safe where things might explode.
Aluminum bronze does not carry electricity as well as copper or brass. The chart below shows how well different metals carry electricity:
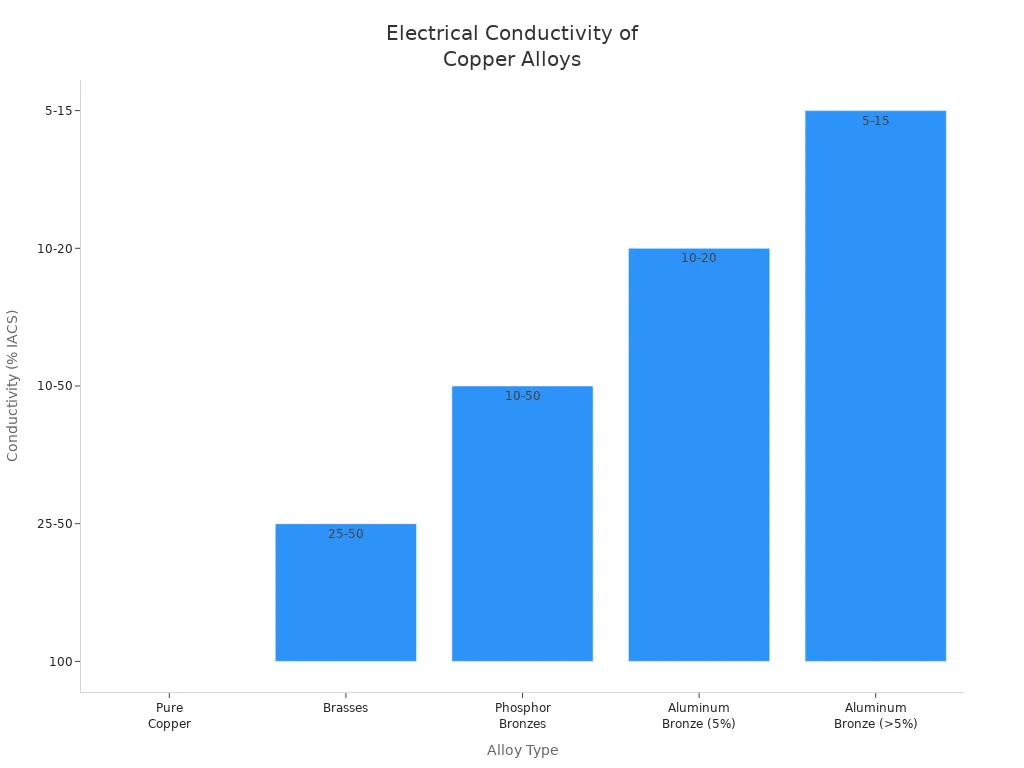
Alloy Type | Electrical Conductivity (% IACS) |
|---|---|
Pure Copper | ~100% |
Brasses | 25% to 50% |
Phosphor Bronzes | 10% to 50% |
Aluminum Bronze (5%) | 10% to 20% |
Aluminum Bronze (>5%) | 5% to 15% |
Even though it does not carry electricity as well, aluminum bronze is still useful. It is used when strength and rust resistance are more important. It is found in bellows, springs, washers, and connectors. These parts work well in tough or wet places. They last longer than copper or brass parts in the same spots.
Aluminum bronze is a good pick for electric parts in wet or salty places. It lasts long and does not rust, even if it does not carry as much electricity.
Aluminum bronzes are different from other bronzes. They are strong, hard, and do not rust easily. They have 3% to 12% aluminum. Tin bronzes have 6% to 19% tin instead. This change in what is inside makes them act very differently.
Property / Alloy Type | Aluminum Bronze | Tin Bronze |
|---|---|---|
Composition | 3% to 12% Aluminum | 6% to 19% Tin, 80-90% Copper |
Tensile Strength (psi) | 65,000 to 80,000 | 30,000 to 40,000 |
Yield Strength (psi) | Up to 40,000 | 12,000 to 18,000 |
Elongation (%) | 12% to 20% | 10% to 20% |
Hardness (BHN) | 125 to 170 | 60 to 80 |
Corrosion Resistance | Very high, especially in seawater | Good, best for moderate loads |
Typical Applications | Marine propellers, gears, landing gear | Bearings, pump bodies, moderate gears |
Aluminum bronzes are much stronger than tin bronzes. They are also harder and last longer in salty water. That is why people use them for ships and heavy machines. Tin bronzes are good for parts that do not get pushed too hard.
Aluminum bronzes cost more than regular bronze. They are more expensive because they have more copper and special features. People pay extra for aluminum bronzes since they last longer and need less fixing.
Aluminum bronzes are pricier than other bronze alloys.
Bronze alloys usually cost 5 to 10 times more than aluminum.
The price changes with copper and tin costs, how they are made, and how hard the part is to make.
Aluminum bronzes are worth the price for ships, oil, and chemical jobs.
Aluminum bronzes are a better deal for tough places, even if they cost more at first.
Engineers use aluminum bronzes when they need strong metal that does not rust. These alloys work best where other bronzes might not last.
Pick aluminum bronzes for ship parts like valves, propellers, bushings, and bearings.
Use them for gears, wear plates, and valve parts that get heavy use.
Nickel aluminum bronze is best for ship propellers and airplane landing gear.
They are good for oil, gas, and chemical plants where saltwater or chemicals can hurt other metals.
They last a long time and do not need much care, so the higher price is worth it.
Selection Criteria | Explanation and Engineering Relevance |
|---|---|
Corrosion Resistance | Great in seawater and chemicals, perfect for ships and chemical plants. |
Mechanical Strength | Very strong for gears, couplings, and impellers. |
Wear Resistance | Lasts longer in mining and moving materials. |
Environmental Durability | Handles saltwater, chemicals, and heat well. |
Precision Engineering | Can be made into exact shapes and sizes. |
Alloy Composition | Aluminum, nickel, and iron make it stronger and stop rust. |
Resistance to Cavitation | Protects ship propellers and pumps from wearing away. |
Aluminum bronzes are also used in planes and defense. They do not make sparks and are not magnetic, so they are safe for special tools. Some types, like nickel aluminum bronze, are both strong and bendy for hard jobs.
Aluminum bronzes are the best choice for hard work, rough places, and parts that must last a long time.
Aluminium bronze is strong and does not rust easily. It lasts a long time, even in rough places like the ocean or factories. Many companies use it for gears, pumps, and ship parts. The table below shows how it does compared to other copper alloys:
Property | Aluminium Bronze | Other Copper Alloys |
|---|---|---|
Strength | High | Lower |
Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
Wear Resistance | High | Lower |
Engineers pick aluminium bronze for hard jobs. They know it will stay strong and last a long time.
Aluminum bronze has aluminum as its main extra part. Regular bronze usually has tin instead. This change makes aluminum bronze stronger. It also helps it fight rust better. Aluminum bronze does not make sparks. It is also less affected by magnets.
Aluminum bronze makes a thin layer on its outside. This layer keeps away most rust and damage. It works well in salty water and places with chemicals. Many engineers pick it for these reasons.
Yes, it is safe. Aluminum bronze does not make sparks when hit. Workers use it for tools and parts where explosions could happen. It helps keep people and machines safe.
People use aluminum bronze for ship propellers, valves, bushings, and gears. Factories, chemical plants, and airplanes use it too. It is best where strength and rust resistance are needed.
Aluminum bronze lets electricity pass, but not as well as pure copper. It is used for connectors, springs, and washers in tough or wet places. Its main use is for strength and lasting power, not for carrying electricity.